PHYSICAL WELLNESS
your body’s invisible shield
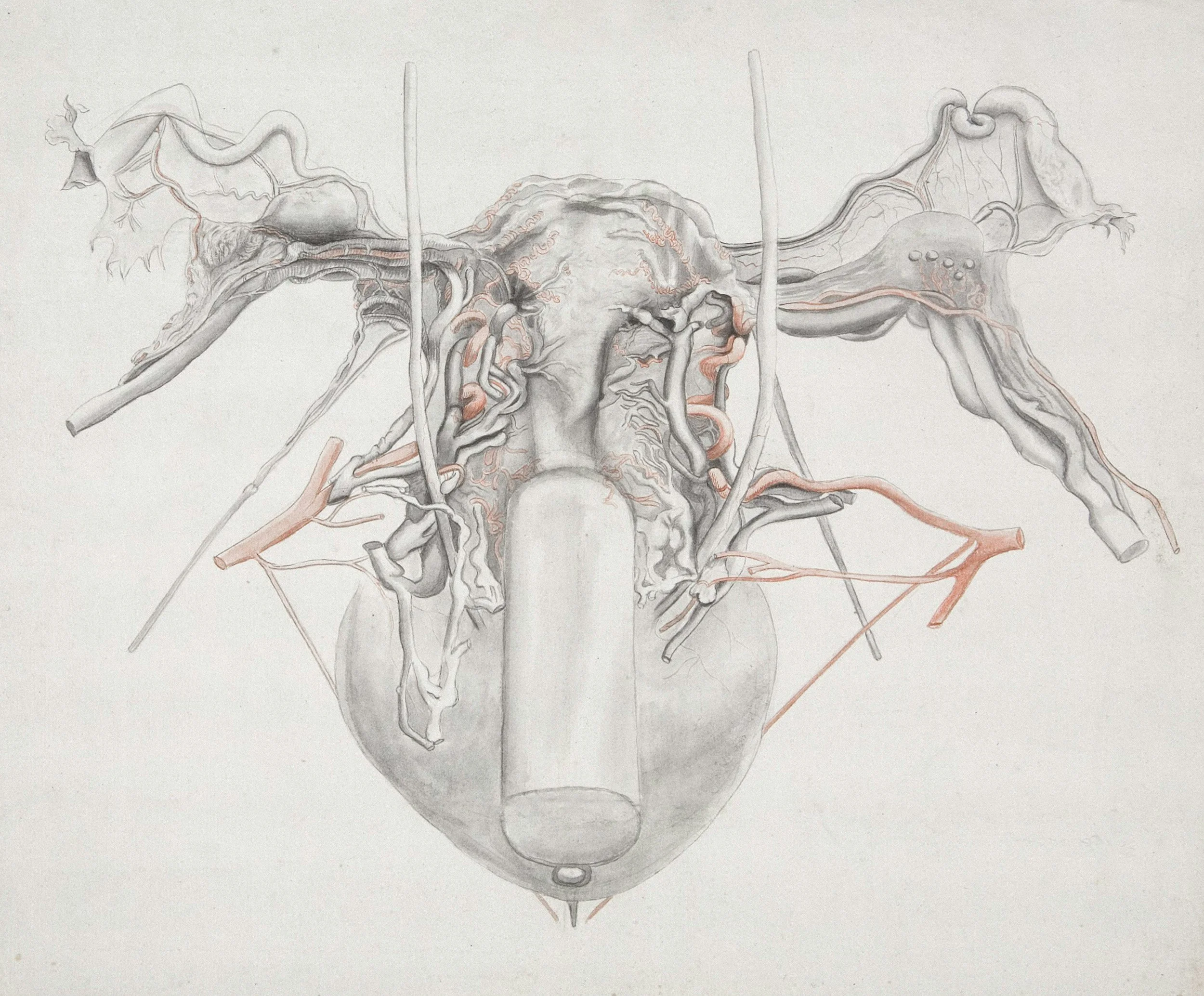
THE FALLOPIAN TUBES
The fallopian tubes are two narrow, flexible tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They are the passageways through which eggs travel after being released from the ovaries. Fertilization of the egg by sperm usually happens here.
Carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus
Provide the site where sperm and egg meet (fertilization)
Support the early development of the fertilized egg (zygote) before it implants in the uterus
Use tiny hair-like structures (cilia) and muscular contractions to help move the egg along
FALLOPIAN TUBE BASICS
Common Terms + Simple Definitions
Here’s a mini glossary for fallopian tube-related words you’ll see throughout the site:
Ovulation - The process when an ovary releases a mature egg into the fallopian tube, usually once per menstrual cycle
Fimbriae - Finger-like projections at the end of the tube that gently sweep the released egg into the tube
Cilia - Tiny hair-like structures lining the tube that help move the egg smoothly toward the uterus
Fertilization - The moment when a sperm cell meets and fuses with the egg, typically inside the tube
Zygote - The single-cell stage of a fertilized egg, which begins dividing as it travels toward the uterus for implantation
Tubal Blockage - A condition where the tube is partially or fully blocked, which can prevent egg and sperm from meeting
Ectopic Pregnancy - A situation where a fertilized egg implants in the fallopian tube instead of the uterus, which is unsafe and requires medical attention
WHAT THE FALLOPIAN TUBES WORK WITH
THE FALLOPIAN TUBES + OTHER SYSTEMS
Ovaries → Release eggs into the tubes during ovulation
Uterus → Receives the fertilized egg (or unfertilized egg if no conception occurs)
Fimbriae → Finger-like ends of the tubes that catch the egg from the ovary
Sperm → Travel up from the vagina through the uterus to meet the egg in the tube
HealthY FALLOPIAN TUBES…
Healthy fallopian tubes are essential for fertility. Blockages, scarring, or infections (like pelvic inflammatory disease) can prevent eggs and sperm from meeting. Maintaining reproductive health through regular check-ups, practicing safe sex, managing inflammation, and supporting overall pelvic health can help protect the tubes. Balanced hormones, good circulation, and a healthy microbiome also support their function.
