PHYSICAL WELLNESS
your digestive + blood sugar regulator
THE PANCREAS
Your pancreas is like a dual-function kitchen appliance — part food processor, part thermostat.
It helps you digest food and keeps your blood sugar in balance.
It works quietly in the background, but without it, your body couldn’t process nutrients or regulate energy properly.
Your pancreas:
Produces digestive enzymes to break down proteins, fats, and carbs
Releases bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid entering the small intestine
Makes insulin to lower blood sugar after eating
Makes glucagon to raise blood sugar when it gets too low
Helps maintain steady energy levels throughout the day
Supports overall metabolism and nutrient absorption
The pancreas isn’t just a digestive helper—it’s also a key endocrine gland. Its hormone-producing cells, called islets of Langerhans, release insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin to regulate blood sugar and overall metabolism.
Insulin Production → Lowers blood glucose by helping cells absorb sugar for energy
Glucagon Production → Raises blood glucose by signaling the liver to release stored sugar
Somatostatin Production → Regulates the release of insulin and glucagon for balance
Helps maintain steady energy levels and metabolic homeostasis
Supports communication with other endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenal, pituitary) through blood sugar regulation
PANCREAS BASICS
Common Terms + Simple Definitions
Here’s a mini glossary for pancreas related words you’ll see throughout the site:
Enzymes - Proteins that break down food into absorbable parts
Bicarbonate - A base that neutralizes stomach acid in the small intestine
Insulin - A hormone that helps move sugar from blood into cells for energy
Glucagon - A hormone that raises blood sugar by releasing stored glucose
Endocrine Function - Hormone production (insulin, glucagon)
Exocrine Function - Enzyme and bicarbonate production for digestion
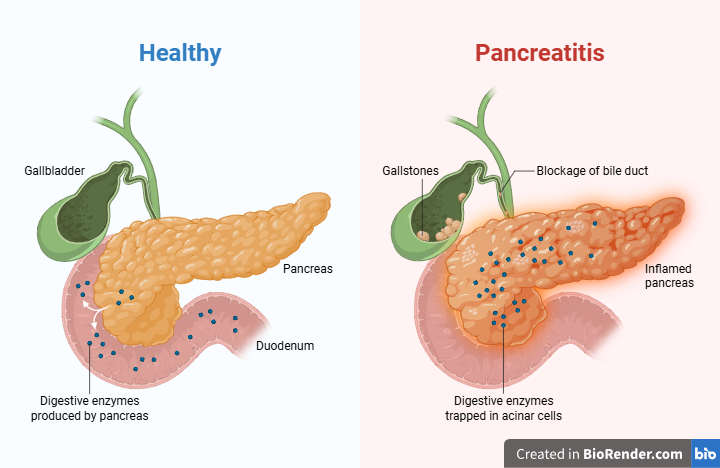
Pancreatitis - Inflammation of the pancreas that can disrupt digestion and blood sugar control
WHAT THE PANCREAS WORKS WITH
THE pancreas + OTHER SYSTEMS
Stomach → Receives chyme and signals the pancreas to release enzymes
Small Intestine → Gets enzymes and bicarbonate from the pancreas for digestion
Liver → Works together to manage blood sugar and metabolism
Gallbladder → Releases bile alongside pancreatic enzymes for fat digestion
Bloodstream → Carries insulin and glucagon to cells throughout the body
Liver → Releases stored glucose when signaled by glucagon
Muscles & Fat Tissue → Absorb glucose in response to insulin
Hypothalamus & Pituitary → Feedback loops help maintain overall energy balance
Adrenal Glands → Cortisol affects glucose levels and energy availability
Digestive System → Works alongside exocrine function for nutrient processing
A healthy pancreas:
Ensures you can digest and absorb nutrients from your food
Keeps blood sugar in a healthy range — preventing crashes and spikes
Supports steady energy and brain function
Helps protect long-term metabolic health
When the pancreas is stressed or damaged, it can lead to poor digestion, nutrient deficiencies, or blood sugar problems like diabetes.
Your pancreas may be small, but it’s a powerhouse of both digestion and energy regulation.
A healthy pancreas keeps blood sugar stable, supports energy, and works in harmony with other endocrine organs. Proper nutrition, blood sugar management, and maintaining a healthy weight help its endocrine function thrive.