PHYSICAL WELLNESS
your body’s immune defense squad
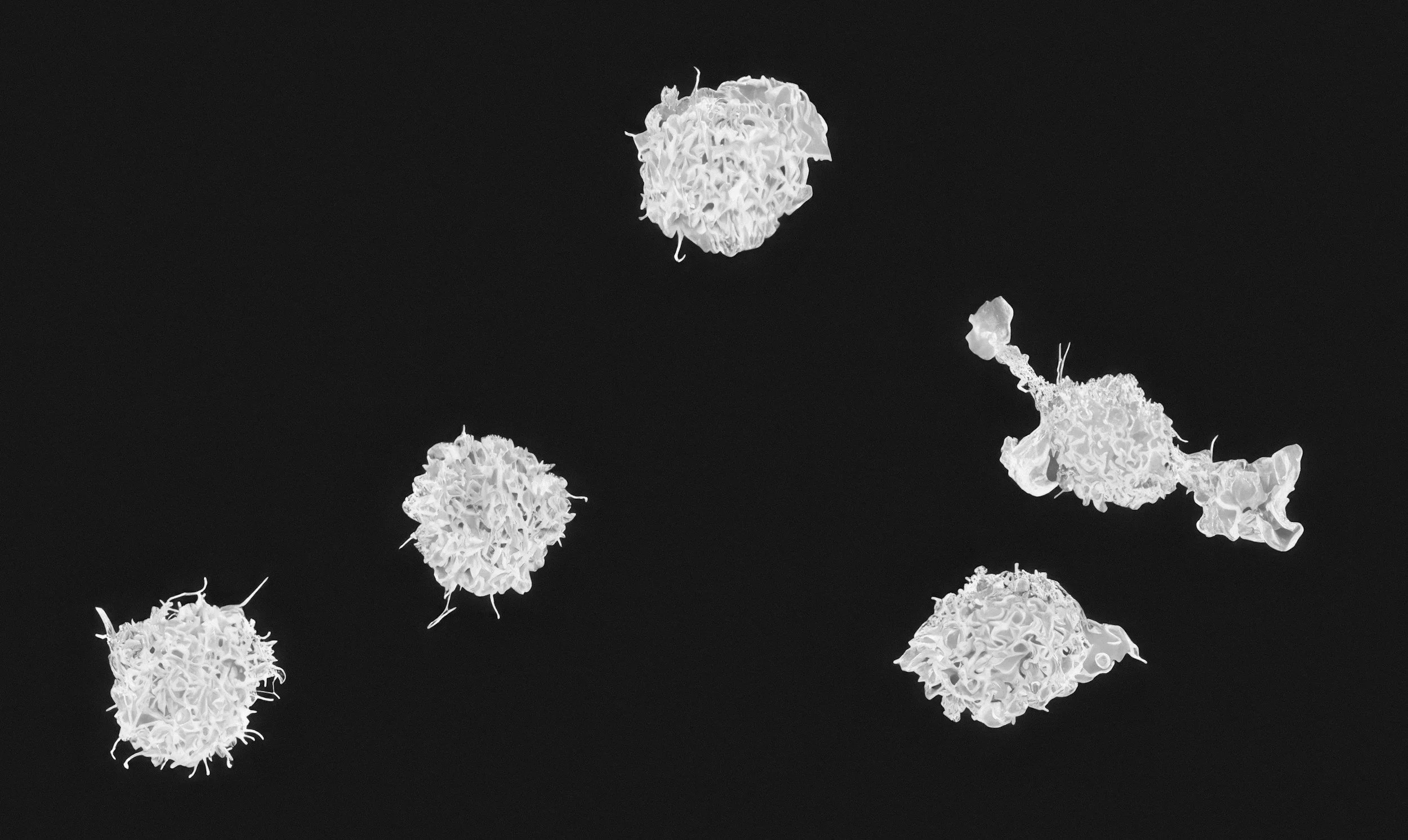
WHITE BLOOD CELLS
White blood cells (WBCs) are like your body’s security team and emergency responders.
They patrol your bloodstream and tissues, looking for anything harmful — and jump into action the moment a threat is detected.
Different white blood cells have different “jobs,” but they all work together to keep you safe and healthy.
Here’s what they help with:
Detect viruses, bacteria, parasites, and other invaders
Destroy or neutralize harmful pathogens
Create antibodies to target specific threats
Remember past infections so they can respond faster next time
Coordinate the immune response (alert other immune cells)
Clean up damaged cells and debris after infection or injury
WHITE BLOOD CELL BASICS
Common Terms + Simple Definitions
Here’s a mini glossary for brain-related words you’ll see throughout the site:
Leukocyte - Another name for a white blood cell
Neutrophil - Fast-acting WBC that attacks bacteria
Lymphocyte - Includes T-cells and B-cells — target specific invaders and build memory
Macrophage - “Big eater” cell that eats and destroys pathogens and debris
Natural Killer (NK) Cell - Destroys infected or abnormal cells (like cancer cells)
Antibody - A protein that tags invaders so WBCs can attack
Cytokine - A signaling molecule that guides and coordinates immune responses
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes) - The body’s defense cells against infection
Monocytes - Clean up debris and fight long-lasting infections
Eosinophils - Target parasites and control allergic responses
Basophils - Release histamine during allergic reactions
WHAT WHITE BLOOD CELLS WORK WITH
white blood cells + OTHER SYSTEMS
Bone Marrow → Produces new white blood cells
Lymph Nodes → Store and activate WBCs during infection
Spleen → Filters blood and helps fight infection
Bloodstream → Transport WBCs to where they’re needed
Antibodies → Work with certain WBCs to identify specific invaders
Cytokines → Chemical messengers that tell WBCs where to go and what to do
Plasma → Carries WBCs throughout the body
Platelets → Work together during injury (WBCs defend, platelets clot)
Lymphatic System → Stores and circulates certain WBCs
Healthy white blood cells
Keep infections under control
Help you recover faster from illness or injury
Protect you from abnormal cell growth
Build immune memory so your body responds smarter next time
Support overall immune balance and resilience
When white blood cells are low, overactive, or confused, it can lead to infections, inflammation, or autoimmune reactions.
Your white blood cells are your frontline defenders — quiet, constant, and essential to staying well.
